1.1 Educational and Instructional Technology – Meaning, Nature, Scope, Definition, Objectives and Significance
The Five generations of ET
1.
The Gurukul System of et
2. Institutional based class room oriented et
3.Distance learning or independent learning
4. Use of media and computers in education and training
5. Internet based learning
Commission on Instructional Technology, U.S.A.
“Educational technology is a systematic way of designing, implementing and evaluating the total process of learning and teaching in terms of specific objectives, based on research in human learning and communication and employing a combination of human and non- human resources to bring about more effective instruction.”
Learning Objectives of Educational Technology
· To identify the educational requirements and desires of the community.
· To understand the structure of education, board strategies, and its goals.
· To design and develop curriculums involving art, science and human values.
· To support strategies and human resources and material assets with the mission to achieve determined goals.
· To create appropriate aids and instruments supporting educational purposes.
· To design educational technology models catering to improve the existing process of teaching and learning.
· To identify and find remedies to tackle major environmental constraints.
· To expand and support educational opportunities for people around the world, especially the neglected sections of the community.
· To manage the entire educational system starting from planning to execution, implementation, and evaluation.
Scope
The objectives of educational technology are process-oriented. The use of educational technology is not restricted to teaching and learning methodologies and theories, but to provide in-depth assistance in the development of an individual’s personality. Below is a list on the wide scope of education technology:
· Educational technology makes the teaching-learning process more efficient and process-oriented.
- Mechanical and electronic gadgets can be readily utilized for educational requirements.
- Educational technology has improved the learning process for students with the help of teaching aids and programmed instructional material, etc.
- Traditional mediums like television, radio, tape-recorder, V.C.R, and computers can be used to impart distance and correspondence education.
- The advancement of the internet has increased education dissemination all over the world with much ease.
- Mechanism of feedback through the use of technology improves the quality of teachers training in academic institutions.
- Technology-driven innovative analytical tools and instruments can help in solving educational administrative problems.
- Educational technology serves to develop and understand the structure and nature of teaching.
- Best utilisation of education technology supports the scientific foundation and new discoveries.
The Nature of Educational Technology
· To understand the nature of educational technology, let us try to view from the following angles:
· Evolution of the concepts of educational technology.
· Existing positions and latest concepts.
· Distinction from the related concepts
Uses Of Educational Technology
· Effective instruction
· Facilitating individual differences
· Providing equal educational opportunities
· Preservation of knowledge
· Transmission of knowledge
· Imparting quality education
· Educational planning
· Pre- service and in- service teacher education
· Finding solutions for Indian educational system
Three main types of technology strategies used for children with special needs: “low” technology, “mid” technology, and “high” technology.
“low” technology
· Not battery powered or electronically operated.
· “low” technology strategies are usually low in cost and easy to use.
· Picture Exchange Communication Systems, Dry Erase Boards, Clip Boards, Laminated Photographs, Manipulative/Objects.
· Aim:- to enhance expressive and receptive communication skills
“Mid” technology
· Require the use of batteries or basic electronic devices such as Voice Output Communication Aids- Big Mack, Talk pad, voice in box
· (piece of equipment that records voice and activated by touch)
· Language Master (cards with recordable strips are run through the machine), Tape Recorders, Braille Embosser
· Aim:-to increase classroom participation, to focus attention on various skill areas, and assist in the development of social skills.
“High” technology
· Usually the most expensive and complex to use.
· Video Taping, Computers, Adaptive Hardware, Touch Window, Big Keys, Trackballs, Software, Accessory Equipment, Digital Cameras, and Scanners.
· Aim:- to increase Receptive Language Skills, Expressive Language Skills, Emotions, Social Skills, Nonverbal Cues, Scripts, Self-help Skills, and Academics, Writing skills, creating written stories
Instructional Technology: Instructional technology is the branch of education concerned with the scientific study of instructional design and development. The main purpose of instructional designers is to create engaging, effective learning experiences.
“Instructional Technology is the theory and practice of design, development, utilization, management, and evaluation of processes and resources for learning” – Association for Educational Communications and Technology
Scope of Instructional Technology
· Determination of Objectives
· Improvement in Teaching Learning Process: 3. Development of Teaching Learning Material
· Improvement in Teaching Training
· Development of Teaching Learning Strategies
· Proper Use of Audio Visual Aids
· Utilization of the Sub-System of Education
· Development of Curriculum
· Proper Use of Hardware and Software
· Provides Feedback
1.2 Educational Technology and Instructional Technology – Role and Recent Trends.
Role of Educational and instructional Technology
1. has provided a scientific base to the educational theory and practice. It has transformed a passive classroom to an active and interactive classroom, with audio-visuals, charts and models, smart classrooms and e-learning room which has drastically motivated and increased the attention level of the students.
2. The introduction of educational technology has modernised the teaching-learning climate of the educational institutions. The learners to be exposed to professionally designed programmes on video or computers.
3. Educational technology has helped and supplemented the teachers in their instructional programmes through the structured lessons for remedial, enrichment or drill purposes. The learners get training for self instruction and teachers are relieved of the burden of routine repetition for exercise and revision purposes.
4. Through a systematic organisation of content and instructional materials, educational technology has provided well-integrated structured materials for teachers thus saving a lot of their time which in turn may be utilized for creative work and quality improvement.
5. The training and use of educational technology contributes towards the professional growth of teachers. It equips them in the use of scientific methods for solving educational and administrative problems. It adds to the teaching competence of teachers and inculcates a scientific outlook and scientific temper in teachers and students.
6. has improved the teaching-learning process and made it more effective and process oriented. Television, Radio, V.C.R, Computers and LCD projectors etc. have enriched and facilitated effective transmission of knowledge.
7. has not only maintained the standards of education but also improved the ways of teaching by giving it Teaching Aids and Programmed Instructional Material.
8. Mechanism of feedback devices for modification of teaching-learning behaviour have produced effective teachers in the teacher-training institutes.
9. Students who appear for higher or competitive examinations have been benefitted by educational programmes on T.V, Radio and Internet.
10. has opened up new fields of educational researches in the field of examination process, evaluation and classroom-teaching.
11. has provided practices and strategies that help teachers to teach according to individual differences of learners.
12. has provided scientific foundation to education through the theories of learning and intelligence.
Recent Trends In Educational And Instructional Technology
App (Application) — This is a piece of software often with quite limited capabilities that can be found on various phones or other portable devices. They are often free, or very cheap, but can also work on a model of ‘in app’ purchases where you can buy add-ons to the original software. They were originally associated with smartphones and tablets, but the term is now used to refer to software in general.
Analytics — This concept is linked to growth of data available in the world that is increasingly used to measure academic performance. As we increasingly interact with technology and that technology records what we do and can measure the amount of time someone interacts with material, how they progress through it, how well they do in a test or activities, then an analysis of this data can give information on how well a person is doing. This information is increasingly displayed on ‘dashboards’ that give a graphical representation of someone’s activity or performance.
Augmented reality (AR) — When a mobile with the right app installed is pointed at an object phone like a picture, that has a trigger connected to it, additional material will be loaded on to the mobile device. So you may have a picture on the wall of the classroom of various famous tourist sites around the world. Pointing the mobile phone at the picture will bring up additional information.
Bring your own device/technology (BYOD/T) — This is a growing and developing practice where learners are encouraged to use their own mobile technologies in or outside of the classroom. It is predicated on the idea that many learners have smartphones, tablets and laptops and the school or college provides connectivity via Wi-Fi.
Community of practice (CoP) — A term that is used to describe a group of people who work together as a learning community. Term originally coined by Etienne Wenger.
e-Portfolio — A piece of software that allows the storage of different types of learning materials that can then be shared. Allows learners to record their learning journey, reflect on progress and for teachers and potentially parents and employers to see how a learner has progressed.
Flipped classroom — A term in current use to describe the previewing of (mostly) video material before a class, so that time in classroom can focus on discussion or activity rather than being given content by the teacher.
Gamification — This is where elements of digital games are applied to the classroom, so in a digital game you have to score a certain number of points before you can progress to the next level, but you can work through the level as many times as you like. Their use is often seen as quite behaviouristic and digital game designers argue that gamification is not the core of what gaming is about.
Google Drive, Google webpages and Google classroom — A collection of useful tools provided by Google in which you can create different kinds of documents which are stored online (in the cloud). Documents are of various types, but they are built so that it is easy to share documents and work collaboratively. Google webpages allow you to quickly create webpages and Google classroom provides a way of linking up all the other tools into groups, monitoring progress, etc. Google classroom needs to be set up at an institutional level.
Infographics — A way of summarising and presenting data using easy-to-read charts and small pictures. These days associated with specific pieces of software that support the development of the infographics.
Interactive whiteboard (IWB) — An electronic whiteboard that is touch-sensitive and is used in combination with a projector to show various kinds of material in the classroom that can be interacted with using the touch-sensitive surface. Most IWBs come with specialised software that enable teachers to create their own materials. They have linked speakers. Many publishers have produced digital versions of their textbooks that include different kinds of activities that make use of the IWBs features.
Learning Management System (LMS) — These are sometimes called virtual learning environments (VLEs) and are essentially a collection of tools, like forums, assessment tools or content display tools, that enable teachers or publishers to collect a number of materials in one place. They can be monitored to check on access.
Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) — These are (mostly) freely available courses produced by universities across a range of subjects. They usually consist of a combination of video materials with associated discussion forums and some form of testing, usually in the form of multiple choice questions. Courses are usually taken by large numbers of people at the same time, so they are essentially self-study.
Podcasts — These can be audio or video. They are essentially a recording of a talk, discussion, lecture, a demonstration of a process or a story. Audio podcasts are easy to distribute on a variety of mobile technologies including MP3 players and phones. Video podcasts are often streamed, but can also be made available offline either by downloading them when there is access to the internet or on SD cards.
QR (Quick Response) codes — These are like a bar code and allow a quick link to some ready-made materials. They are added to coursebooks to extend the content. They are being replaced by augmented reality triggers.
Social networking tools — There are many of these, including Facebook, WhatsApp and WeChat. These allow the creation of communities who can exchange ideas on a variety of topics. They have essentially replaced earlier tools like discussion forums. A tool like WhatsApp has the advantage over a public tool like Facebook that it is a closed community.
Video conferencing tools — A range of different tools exist, including basic ones like Skype or more sophisticated online classroom tools like Adobe Connect.
Virtual reality (VR) — A 2D or 3D online environment where you can engage in activity that you would do in the real world, like visit a museum, or something it would be impossible to do, for example to go inside a volcano, and get an idea of what these environments are like. Virtual reality tools are used also for training people in skills like surgery or building construction.
Wiki — A webpage environment that anyone who is given access to it can edit the pages.
1.3 Approaches of Educational Technology – Hardware, Software, System approach, Individual & Mass media approach.
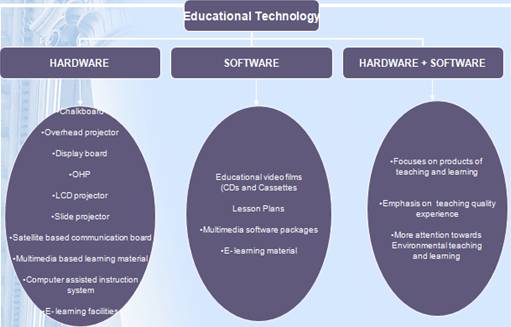
Hardware Approach of Educational Technology
The hardware approach refers to the use of machines and other mechanical devices in the process of education. Its origin lies in the application of “physical science” to education and training system. The process of teaching-learning has been gradually mechanized through the use of teaching machines, radio, television, tape recorder, video-tape, projectors etc. The teacher can deal with a larger group of students at the same time by his discourse through these machines.
The hardware approach is based on the application of engineering principles for developing electro-mechanical equipment for instructional purposes. Motion pictures, tape recorders, television, teaching machines, computers are called educational hardware.
Hardware approach mechanises the process of teaching so that teachers would be able to deal with more students with less expenditures in educating them.
Human knowledge has three aspects:
· Preservation,
· Transmission and
· Development.
The history of preservation of the knowledge is believed to exist since the printing machines started. The knowledge is preserved with these machines in the form of books which are shelved in the libraries, tape recorders and films.
The second aspect of human knowledge is its transmission. A teacher can impart knowledge himself to his pupils. Now a days, transmission of the knowledge is supported by machine like mike, radio and television. With these, thousands of pupils can enjoy this home-delivery of such benefits.
The third aspect of human knowledge is its development. For this aspect, provisions are made for research work. In the research programmes, the main function is the collection and analysis of data. For this purpose, presently the researcher uses the electronic machines and computers.
Hence, all the three aspects of knowledge allow the use of machines. In short, the teaching process has been mechanized. The mechanization of teaching process is termed as the Hardware Approach.
Basis of Hardware Approach
· Hardware Approach has physical science and applied engineering as its basis.
· Hardware Approach has mechanised the whole teaching-learning process.
· Hardware Approach adopts a Product-oriented Approach.
· Hardware Approach has the potential to hand over the educational benefits to the mass with greater ease and economy.
Characteristics of Hardware Approach
· Silverman , called this type of educational technology ‘Relative Technology’. Based on physical science and applied engineering field approach. The concept of hardware approach is derived from the application of “physical science” to education.
· The new mechanism of teaching-learning with improved technology as its basis. Suggesting innumerable new ways of doing things to the class-room teachers
· The job and the duties of the teacher are likely to have multifaceted changes as they are to deal with many new gadgets for teaching and learning .
· Engineering principles are used for the development of these types of technical equipments. The teacher can deal with larger group of students with the help of these ‘Mechanical device’ or ‘Machines’.
· The teacher can deal with larger group of students with the help of these ‘Mechanical device’ or ‘Machines’ , resulting in less cost and economy in finances .
Software Approach of Educational Technology
The pioneering work in software approach was done by Skinner and other behaviourists. The programmes which such a technology produces are often called software. Software Approach is also termed as Instructional Technology or Teaching Technology or Behavioural Technology.
It originates from behavioural sciences and their applied aspects concerning psychology of learning. The software approach used the principles of psychology for building in the learners a complex repertory of knowledge or modifying his behaviour . Psychology of learning provides solid technology for bringing desirable behavioural changes in the pupils and serves the cause of education of laying down definite instructional procedure, teaching behaviour and behaviour modification devices.
Newspapers, books, magazines, educational games, flash cards may also form part of software. Software approach is characterised by task analysis, writing precise objectives, selection of appropriate learning strategies, immediate reinforcement of responses and constant evaluation.
Software approach refers to the application of teaching- learning principles to the direct & deliberate shaping of behavior. Its origin lies in the application of “behavior science” to the problems of learning & motivation.
Educational technology is closely associated with the modern principles & theories of teaching. Models of teaching, theory of instruction, theory of teacher- behavior & principles of programmed learning. It is characterized by task analysis, writing, objectives in behavioral terms, selection of the appropriate teaching strategies, reinforcement for correct responses & continuous evaluation.
Software Approach is concerned with teaching objectives in behavioural terms, principles of teaching, methods of teaching, reinforcement of instructional system, feedback, reviews and evaluation. Software approach tries to develop all the three basic components of technology, i.e. Input, Process and Output.
Basis of Software Approach
• In software approach, the basis of all thinking and working is behavioural science and psychology of learning.
• Software approach uses the principles of psychology for the purpose of behaviour modification.
• A teacher with added knowledge of software approach can use the films, flashcards, tapes etc., for various purposes.
• A teacher can plan better teaching which results into better learning. There is not end to his thinking.
Characteristics of Software Approach
· This view of educational technology is closely associated with the modern principles of programmed learning and is characterised by task analysis, writing precise objectives, selection of appropriate learning strategies, reinforcement of correct responses and constant education.
· Silverman termed this educational technology as ‘constructive educational technology.’ Also known as ‘Management Technology’.
· A modern approach in educational administration and organisation. It has brought to educational management a scientific approach for solving educational administrative problems.
· Origin of software approach lies in the application of ‘behavioural science’ to the education. It refers to the application of teaching- learning principles in the shaping of behaviour.
· Its application while writing objectives in behavioral terms, selection of appropriate teaching, strategies, reinforcement for correct response etc
Software Tools
Word processing, database, spreadsheet, telecommunications, presentation, authoring, graphic paint programs. Teachers need to know how to use them, how to teach them to students, and how and why to use them in the classroom.
Software Types
Drill and practice, tutorials or computer-based instruction, and simulations. Teachers need to know what these are as well as why, when, and how to incorporate them into their teaching.
Software Review and Evaluation
How to select appropriate software for specific grade levels and content areas, how to evaluate the effectiveness of this software, and what types of software are available. Teachers need to be thoroughly familiar with many of the software options available and understand when and how to use them in the classroom.
Comparison of Hardware and Software Approach

Role of hardware and software technologies in modern educational practices
1. Making the task of teaching-learning interest, purposeful and productive
2. Use the multimedia and multi-sensory approach to teaching-learning
3. Management of the affairs of educational practices in an efficient and productive way
4. Providing proper input and process for the best possible outcomes (products)
5. Fulfilling the expectation of distances and correspondence education
6. Individualization of instruction
SYSTEMS APPROACH:
System approach is a systematic attempt to coordinate all aspects of a problem towards specific objectives. Webster’s dictionary defines a system as “a regularly interacting or independent group of items forming a unified whole.” The characteristics of a system of may be explained with the help of an example – various parts of the digestive system may be called as components of digestive system. Every component of the digestive system contributes to as supports in functioning of the digestive system as a whole.
In the context of education, system is a unit as a whole incorporating all its aspects and parts, namely, pupils, teachers, curriculum, content and evaluation of instructional objectives. The teaching-learning process is viewed as communication and control taking place between the components of a system. In this case, the system is composed of a teacher, a student and a programme of instruction, all in a particular pattern of interaction.
The System Approach focuses first upon the learner and then course content, learning experiences and effective media and instructional strategies. Such a system incorporates within itself the capability of providing continuous self-correction and improvement. It is concerned with all elements of instruction including media, including hardware and software. Its purpose is to ensure that the components of the organic whole will be available with the proper characteristics at the proper time to contribute to the total system fulfilling the objectives.
In the systems approach to instruction, the teacher has to plan completely the utilization of selected resource material and the classroom activities. The teacher should have a good overall view of the subject, know his/her limitations, know all about his/her pupils and the individual differences in their learning capacities and plan accordingly. The system approach involves continuous evaluation of learning outcomes and utilization of knowledge gained by analysis of results of evaluation to suitably modify the plan of approach to achieve the stated objectives.
INDIVIDUAL AND MASS- MEDIA APPROACH
The utilization of Mass Media Approach is vital importance for achieving the goal of education for all. In rapidly increasing availability of new, improved channels of communication has contributed to a coordinated spurt in effort to tap a harness the vast potential of media in promoting the goal of Education for all. In a country such as India-so-replete with challenging regional cultural and linguistic diversities the role of Media as an immensely powerful tool which can be used to penetrate cultural and attitudinal barriers and reach communities in the shortest possible time acquires a significance that is doubly important.
Importance Of Mass Media
• Mass Media provide information to the mass within a less time.
• It takes a wide coverage of information regarding anything that is happening in any comer of the world.
• It brings the entire world to the individual or to the classroom. Children spend hours together sitting in front of the television and can visualize, hear and acquire knowledge about the world.
• These media easily reach groups, allow repeated use, give more reality, influence attitudes, show cause and effect relationships and ultimately motivate the audience.
• It sends information to remote places and helps in distant learning.
• It helps in modification of attitudes, inculcation of desirable values and acquaintance with cultural heritage.
• Mass media acts as an agency of social change.
• Mass media are useful for reinforcing group dynamics and interpersonal communication.
• Mass media as means of communication make ideas clear to children and help them to acquire correct knowledge. They help in simplifying and in giving vividness to explanation.
• Mass Media make the instruction concrete and stimulate interest and excite curiosity in things.
Demerits Of Mass Media
Sometimes, mass media creates misunderstanding among the people providing false and baseless news. Besides, satellite channels often telecast some vulgar programs that damage the moral character of the young generation. People who watch violent films through mass media, commit crimes easily and engage themselves in illegal works. It is true that people regularly exposed to violent media usually grow up to be completely normal people. But, the number of these people is very few because all people of a country or society do not follow or observe mass media. Besides, a large group of people in a society is out of modern technology.
1.4 Differential Instruction, Universal Design of learning and Individualised Instruction.
Differentiated instruction: Planning for all
• Differentiated instruction is an organizing structure or framework in teaching and learning which calls for a major restructuring in the classroom and curriculum, if done well, its benefits far out way the costs. “Differentiated instruction can be defined as a philosophy of teaching that is based on the premise that students learn best when their teachers accommodate the difference in readiness levels, interests and learning profiles. “Differentiated instruction is a process to teaching and learning for students of differing abilities in the same class. The intent of differentiating instruction is to maximize each student’s growth and individual success by meeting each student where he or she is and assisting in the learning process8”. Differentiated instruction seeks to move away from teaching to the whole class in the same manner and addresses the needs of all learners, including those who are at risk and the gifted, through various forms of well planned, well-organized, flexible curriculum and instructional strategies. Differentiated instruction can enable students with a wide range of abilities—from gifted students to those with mild or even severe disabilities—to receive an appropriate education in inclusive classrooms. In order to understand differentiated instruction, the principles for practicing must be articulated viz.
• Every child can learn.
• All children have the right to high quality education.
• Progress for all will be expected, recognized and rewarded.
• Learners in a classroom have common needs, distinct needs, and individual needs”.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a set of principles that guide the design of inclusive classroom instruction and accessible course materials. UDL’s three principles are: 1) multiple methods of representation that give learners a variety of ways to acquire information and build knowledge; 2) multiple means of student action and expression that provide learners alternatives for demonstrating what they have learned; and 3) multiple modes of student engagement that tap into learners’ interests, challenge them appropriately, and motivate them to learn
Principles of Universal Design
ü Equitable use
ü flexibility in use
ü simple and interactive use
ü perceptible information
ü tolerance for error
ü low physical effort
ü Size and space for approach and use
Individualized Instructions
Individualized Instruction is a method of instruction in which content, instructional technology (such as materials) and pace of learning are based upon the abilities and interests of each individual learner. Let’s learn about individualized Instruction in greater detail and how educators can provide it to students by using the 21st century technology.
Individualized Instruction (also called Differentiated Instruction) is an instructional theory that allows educators to face nowadays’ educational challenges by considering diverse student factors while planning curriculum and delivering instruction. The factors include learning styles, learning abilities, interests, etc., of each individual student found within a classroom. Old traditional classroom methods aren't enough to provide students with Individualized Instruction. So, 21st century teachers are searching for many technological approaches that drive them to provide students with multiple learning approaches.
Individual Instructions for students with different learning styles:
As mentioned above, different students have different learning styles. Some students learn by visualizing, some by hearing, some by reading while many others do so by experimenting. Technology helps educators to provide students with resources that help them adopt their own learning style. A list of such resources is as follows, explore them to provide each learner with the respective technological approach.
Visual Learning:
Visual learning is a learning style in which ideas, thoughts, concepts, processes and other information are represented and associated with images, graphs, charts and videos. Students understand and learn just by visualizing.
Auditory Learning:
Auditory learning is a learning style in which students learn by hearing.
Kinesthetic Learning: It’s a learning style where learning is done by experimentation.
Special education is a great example of individualized instruction. Students who receive special education services have an Individualized Education Program (IEP). Through an IEP, the school can meet their individual needs and provide accommodations just for them.
1.5 Implication of the above for inclusion.
In today’s society of informational instant gratification, people have begun to gain knowledge through the internet, television and other types of media. It has become apparent that society as a whole is changing the way it gathers and stores information. Although some still gain their information through newspapers and books many have shifted to more easily accessible forms of data gathering. One area where technology has caused a large shift is in the field of education. With the number of students inundated with smart phones, students are one touch away from the internet, music, Facebook, Twitter and YouTube videos. This increase has become quite a challenge for educators to keep up with various forms of media that are interesting to students while still allowing the transmission of non-watered down material. With new educational technologies such as Smart Boards becoming an everyday staple of the classroom it has become imperative that educators not only possess this new technology, but more importantly be able to navigate through and manipulate this technology to best meet the needs of their students. If teachers are not feeling prepared for this task, educational administrators need to ensure the success of all teachers both young and old and provide them with professional development opportunities. ChanLin (2007) states, “There is a consensus among educators and various social communities that current educational practices need to prepare students to thrive in an ever changing technological society”. This means that in order for students to be successful in a global economy based on growing informational technologies, it has become more and more important for students to have exposure to various media types.
Today Technological efforts for PwD
· Government and non-Governmental organizations funded by MSJ&E
· NIMH developed software's packages for children with Mental Retardation. a) Literacy, b) Numeracy, c) Number skills, d) My country, e) Living and non-living things, f) Health and safety and g) Community utilization
· National Association For Blind
o Screen reader software in different Indian languages
o PC support for windows environment
Media Lab Asia
· National Disability Register, Online courses by RCI and RCI Studio
· ICT based Punarjjani: Assessment and Analysis for PwMR
· Sanyog: A multilingual augmentative and alternative communication system.
o Construct simple sentences by selection of Icons.
· Smart Cane: Bus identification system based on wireless communication technology such as route number and Bus stop.
· Shruti: A computer aided text-to-speech and text to Braille system (Hindi and Bangla)
o Available for Windows
DAISY (Digital Accessible Information system)
A world where people with print disabilities have equal access to information and knowledge, without delay and additional expense.
· DAISY Books with >18 languages,
· Braille in DAISY,
· synchronized text and audio, multimedia reading experience (completely accessible).
· Yahoo India Accessibility Lab
· (web accessibility)
· Barrier Break Technology
· ( Firm that provides solutions for PwD and distributor)


