2.1 ICT – Meaning, Definition, Scope and Significance
ICTs stands for information and communication technologies
and are defined, for the purposes of this primer, as a ’diverse set of technological
tools and resources used to communicate and to create, disseminate, store and
manage information.
ICT is considered to be dynamic in nature, which in turn makes vital changes in
the society. ICT has influenced all aspects of life. It provides various
opportunities in adapting teaching, learning and managing the individual needs
of both teacher and students. It helps in reducing the challenges being faced
by the educational system of India. These technologies are different because of
their fast evolution and revolution. The beginning of computer and now ICT has
showcased various impacts on learning. In the current age of information,
educational institutions are expected to play a crucial role for learning
environment and knowledge generation and ICT helps in facilitating this task.
It becomes one of the most effective factors in the school improvement.
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
According to UNESCO, "ICT is a scientific, technological and
engineering discipline and management technique used in handling information
and association with social, economic and cultural matters."
ICT refers to technologies that provide access to information through
telecommunications. It is similar to Information Technology (IT), but focuses
primarily on communication technologies. This includes the Internet, wireless
networks, cell phones, and other communication mediums. Jan 4, 2010
With knowledge come learning, skills, adaptability, understanding and
activism-all factors that contribute to the growth of an equitable society. ICT
offers the means to acquire this power. Since knowledge is vital, it follows
that the acquisition of knowledge must be lifelong.
The National curriculum framework (NCF) 2005," ICT is an important tool
for bridging social divides. ICT should be used in such a way that it becomes
an opportunity equalizer by providing information, communication and computing
resources in remote areas."
CHARACTERISTICS OF ICT
1. Drill and Practice
2. Self pacing
3. Discovery learning
4. Tutorials
5. Stimulation
6. Multimedia effects
Benefits of ICT application in Education
The benefits of ICT application in education can be summarized as bellow:
1. ICT increases the access to education.
2. It improves the quality of education by developing new ways of interaction
and also makes teaching –learning process more interesting.
3. It provides equal opportunities to the large number of learners to obtain
education and information.
4. It provides specialized tools for learners with visual, hearing or mental
impairment, so that they learn and acquire knowledge at their own pace.
5. It provides support to each and every school in sharing educational /
learning experiences with the different schools throughout the country.
6. It enables the distance education system to be more effective.
7. It helps in promoting technology literacy to every citizen and especially to
young stars.
8. It provides opportunities for lifelong educations.
9. It enhances the teacher’s quality both in terms of teaching and research.
2.2 Psychological bases for ICT among teachers and learners
ICT is the basic for educational learning process and human behavior or cognitive psychology. IT is fundamental in the modern education system as instructional design and communication tools, which clearly visualize and understand what learning is with the belief that learners enable and capable of improve the process. Since, learning exhibits itself as a change in behavior and the inference of learning is made by comparing what behavior is possible before the individual is placed in a “learning situation” and what behavior can be exhibited after such a treatment. The paradigm of ICT for behavioral psychology is therefore, it is information-processing principles and techniques as the basis of instructional design. It is the methods to describe educational pedagogy as behavioral changes to develop a human cognitive which linked internal structures to external design of instructional environments.
ICT for education in general is a means of identifying learning desires, capabilities, outcomes (intellectual skills, cognitive strategies, verbal information motor skills and attitude) and another methodology to be acquired by individuals. It is a paradigm technology for learning process makes a difference to instruction. The ICT based learning process is a model of education facilities and memory deriving from cognitive psychology and information-processing theory. Therefore, educational and behavioral psychology is the process of learning events that comprise both internal and external conditions of learning process. By internal is essentially previously acquired concepts and skills and the mental processes and structures used by the learner to develop new concepts and skills based on the recall of prior skills. The external is the learning process taking the form of instruction designed for the acquisition of particular learning outcomes.
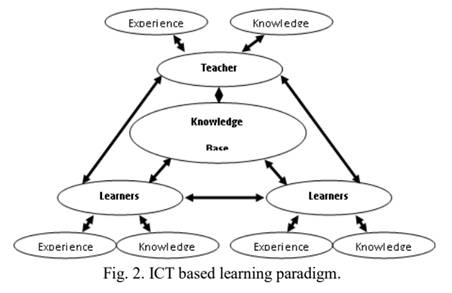
Educational technology is an engine for development; resources use optimization and facilities, access and safety, and also future educational strategic plan. Thus, it is vitally important to learners and/or educators anytime and anywhere, business and other settings. The technology encompasses both educational and developmental material objects, such as machines and networking hardware, as well as theories such as instructional theory and learning facilities. ICT for education is an integral part of societies‟ everyday life, which refers to an array of tools and the principles for their effective application in learning process and facilities. ICT for behavioral and educational psychology is therefore, methodologies and techniques, and skills assessment for learners and educators in their learning provider institutions towards its impacts. ICT as the paradigm of educational and behavioral psychology is a dynamic and multi-factor aspect, including, Internet-based learning and instructional and learning theory, media perception and human social interactions, fields of study that apply human behavior to educational technology.
However, there is a disambiguation about what ICT as educational technology should refer. Especially for young scientists and education experts do have a limitation to define its paradigm roles in education industry. There is a big public debate that refers to all valid and reliable applied education science, such as equipment, as well as processes and procedures that are derived from scientific research. The gap on understanding of educational technology is visualized as it would be science or materials. In this paper, we proposed a novel idea and approaches that reveal its integral aspects to optimize education performance and facilities in the case of material (the hardware devices and infrastructure) and science (instructional and conceptual contents) of modeling of the human behavior and feelings in the learning process. It means; the educational technology in a given context refers to theoretical, algorithmic or heuristic processes, and physical technology. The contribution of the paper is summarized as it is a novel approach to investigate students‟ and teachers‟ technology-related issues, ICT in the learning process and activities and its paradigm impacts on education behavioral and psychological changes.
2.3 Development of ICT – Stages, Requirement and Process
Stages of ICT development

Emerging Stage: Schools at the beginning stages of ICT development demonstrate the emerging approach. Such schools have just started on their journey in the ICT field with a skeleton computing infrastructure either donated or purchased by the school authority. In this initial phase, administrators and teachers just start to explore the possibilities and consequences of using ICT for school management and adding ICT to the curriculum.
Applying Stage: Those schools, in which a new understanding of the contribution of ICT to learning has developed, exemplify the applying approach. In this secondary phase, administrators and teachers use ICT for tasks already carried out in school management and in the curriculum. Teachers largely dominate the learning environment. Schools at the applying approach phase adapt the curriculum in order to increase the use of ICT in various subject areas with specific tools and software such as drawing, designing, modeling and application specific tools.
Infusing Stage: At the third stage, the infusing approach involves integrating or embedding ICT across the curriculum, and is seen in those schools that now employ a range of computer-based technologies in laboratories, classrooms, and administrative offices. The curriculum begins to merge subject areas to reflect real-world applications. In the infusing approach to ICT development, ICT infuses all aspects of teachers' professional lives in such ways as to improve student learning and the management of learning processes.
Transforming Stage: Schools that use ICT to rethink and renew school organization in creative ways are at the transforming approach. ICT becomes an integral though invisible part of daily personal productivity and professional practice. The focus of the curriculum is now learner-centered that integrates subject areas in real-world applications.
Stages of ICT Usages
Studies of teaching and learning in schools around the world identify four broad stages in the way that teachers and students learn about and gain confidence in the use of ICT. These four stages give rise to the mapping depicted in Figure 2 that shows the stages in terms of awareness, learning how, understanding how and when, and specializing in the use of ICT tools according to the stages of the proposed model.

Becoming aware of ICT: In the initial phase, teachers and learners become aware of ICT tools and their general functions and uses. In this stage, there is usually an emphasis on ICT literacy and basic skills. This stage of discovering ICT tools is linked with the emerging stage in ICT development.
Learning how to use ICT: Following on and from the first stage comes the stage of learning how to use ICT tools, and beginning to make use of them in different disciplines. This stage involves the use of general or particular applications of ICT, and is linked with the applying stage in the ICT development model.
Understanding how and when to use ICT: The next stage is understanding how and when to use ICT tools to achieve a particular purpose, such as in completing a given project. This stage implies the ability to recognize situations where ICT will be helpful, choosing the most appropriate tools for a particular task, and using these tools in combination to solve real problems. This stage is linked with the infusing stage in the ICT development model.
Specializing in the use of ICT The fourth and the last stage involves specializing in the use of ICT tools which occurs when one enters more deeply into the learning environment that creates and transforms the learning situation with the help of ICT. This is a new way of approaching teaching and learning situation with specialized ICT tools and is linked with the transforming stage in the ICT development model.
Pedagogical Usages of ICT
Supporting work performance: In the initial phase, teachers use productivity tools such as word processor, visual presentation software, spreadsheet, database, email etc. to support their daily work performance. In this initial stage, there is usually an emphasis on basic operations of electronic office software. This stage of using productivity tools for teaching and learning is linked with the emerging stage in ICT development.
Enhancing teaching: Following on and from using productivity software, comes the stage of learning how to use and develop computer assisted learning software and beginning to make use of such software in different disciplines. This stage involves the technique of integrating computer-based learning in the traditional instructional process, and is linked with the applying stage in the ICT development model. Various instructional packages were selected, developed and used to enhance traditional classroom teaching.
Facilitating learning: The next stage involves using various types of instructional software to facilitate student learning. The key point is that the teachers need to learn how to choose the most appropriate tools for a particular task, and using these tools in combination to solve real life problems. This stage implies the ability to recognize situations where various multimedia, simulation and modelling software can be utilized for teaching and learning. This stage is linked with the infusing stage in the ICT development model.
Creating innovative learning environments: The fourth and last stage involves specializing in the use of network based resources to create meaningful environment with rich affordable for innovative learning models so that it occurs when one enters more deeply into the shared learning environment that creates and transforms the learning situation. This is a completely new way of approaching teaching and learning using technology. It helps to develop, deliver and manage open & flexible learning program. This stage is linked with the transforming stage in the ICT continuum model.
2.4 Use of ICT in developing collaborative networks for sharing and learning such as Internet – E-mail, Tele-teaching, Tele-conference
Teleconferencing means meeting through a telecommunications medium. It is a generic term for linking people between two or more locations by electronics. There are at least six types of teleconferencing: audio, audiographic, computer, video, business television (BTV), and distance education. The methods used differ in the technology, but common factors contribute to the shared definition of teleconferencing:
- Use a telecommunications channel
- Link people at multiple locations
- Interactive to provide two-way communications
- Dynamic to require users' active participation
Types of Teleconferences
Audio Teleconference: Voice-only; sometimes called conference calling. Interactively links people in remote locations via telephone lines. Audio bridges tie all lines together. Meetings can be conducted via audio conference. Preplanning is necessary which includes naming a chair, setting an agenda, and providing printed materials to participants ahead of time so that they can be reviewed.
Distance learning can be conducted by audio conference. In fact, it is one of the most underutilized, yet cost effective methods available to education. Instructors should receive training on how to best utilize audio conferences to augment other forms of distance learning.
Audiographics Teleconference: Uses narrowband telecommunications channels to transmit visual information such as graphics, alpha-numerics, documents, and video pictures as an adjunct to voice communication. Other terms are desk-top computer conferencing and enhanced audio. Devices include electronic tablets/boards, freeze-frame video terminals, integrated graphics systems (as part of personal computers), Fax, remote-access microfiche and slide projectors, optical graphic scanners, and voice/data terminals.
Audiographics can be used for meetings and distance learning.
Computer Teleconference: Uses telephone lines to connect two or more computers and modems. Anything that can be done on a computer can be sent over the lines. It can be synchronous or asynchronous. An example of an asychronous mode is electronic mail. Using electronic mail (E-Mail), memos, reports, updates, newsletters can be sent to anyone on the local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN). Items generated on computer which are normally printed and then sent by facsimile can be sent by E-Mail.
Computer conferencing is an emerging area for distance education. Some institutions offer credit programs completely by computer. Students receive texts and workbooks via mail. Through common files assigned to a class which each student can assess, teachers upload syllabi, lectures, grades and remarks. Students download these files, compose their assignment and remarks off-line, then upload them to the common files.
Students and instructors are usually required to log on for a prescribed number of days during the week. Interaction is a large component of the students' grades.
Through computers, faculty, students and administrators have easy access to one another as well as access to database resources provided through libraries. The academic resources of libraries and special resources can be accessed such as OCLC, ERIC, and Internet.
Administrators can access student files, retrieve institutional information from central repositories such as district or system offices, government agencies, or communicate with one another. Other resources can be created such as updates on state or federal legislation.
Video Teleconference: Combines audio and video to provide voice communications and video images. Can be one-way video/two-way audio, or two-way video/two-way audio. It can display anything that can be captured by a TV camera. The advantage is the capability to display moving images. In two-way audio/video systems, a common application is to show people which creates a social presence that resembles face-to-face meetings and classes and enables participants to see the facial expressions and physical demeanor of participants at remote sites. Graphics are used to enhance understanding. There are three basic systems: freeze frame, compressed, and full-motion video.
Video conferencing is an effective way to use one teacher who teaches to a number of sites. It is very cost effective for classes which may have a small number of students enrolled at each site. In many cases, video conferencing enables the institution or a group of institutions to provide courses which would be canceled due to low enrollment or which could not be supported otherwise because of the cost of providing an instructor in an unusual subject area. Rural areas benefit particularly from classes provided through video conferencing when they work with a larger metropolitan institution that has full-time faculty.
Through teleconferencing, institutions are able to serve all students equitably.
Teleteaching
· Teleteaching can be considered as a form of e-learning or distance teaching. Most often, it implements a sort of direct instruction approach.
· Sometimes it also is used as synonym for educational videoconferencing, i.e. as a component of a design, not a design by itself.
A key feature of a teleteaching instructional design model is e-instruction. Teleteaching is most often done in a class context (i.e. learners connect at the same time and can interact with the instructor). But they also may choose to look at archived sessions they can download. In addition, each learner will have to work on his own.
Internet –Email
Millions of computer all over the world are connected through the Internet. Computer users on the internet can contact with one another anywhere in the world.
Uses and advantages of internet File transferring facility.
1.Reach to the world wide viewers.
2.Effective, easier, faster and cheaper promotion of product or service.
Misuses and disadvantages of internet
1.Stealing, modifying or destructing data.
2.Piracy of software, audio, video or other intellectual contents.
Electronic mail (email) is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more persons. Email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Many people sign up for internet services just so that they can send and receive e-mail messages. It is probably the most used feature of the web.
2.5 Use of ICT to simplify record keeping, information management in education administration in special and inclusive settings
Use of ICT on Records Management
Change has been happening at an uneven pace in any growth-oriented industry, and the education sector is no exception. Rapid growth in the field of education has made governance in academic sector a very complex task. The 21st century has witnessed tremendous advancements in technology which has led to far-reaching developments in the administrative system. Cost-effective technology combined with the flexibility in learning and administrative activities is essential to enhance efficiency.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) plays a vital role in supporting powerful, efficient management and administration in education sector. It is specified that technology can be used right from student administration to various resource administration in an education institution
School records are books, documents, files and CD ROM in which is embodied information on what goes on in school (e.g. scholastic, co-scholastic, non-scholastic activities and important events etc), the school plant as well as other relevant information focusing on the growth and development of the school.
The school records are official transcripts or copies of proceedings of actions, events, other matters kept by the school administrator, school records could be viewed as authentic registers or instruments or documents of official accounts of transaction or occurrence which are preserved in the school’s office. Therefore, every school must keep certain specified records.
Importance of school records: School records keeping includes the fact that school records tell the history of the school and are useful historical sources.
· Tell the history of the school and are useful historical sources.
· Facilitate continuity in the administration and management of a school.
· Facilitate and enhance the provision of effective guidance and counselling services for students in the social, academic career domains.
· Provide information needed on ex-students by higher and other related institutions and employers of labour for admission or placement.
· Facilitate the supply of information to parents and guardians for the effective monitoring of the progress of their children/wards in schooling or performance.
· Provide data needed for planning and decision making by school heads, ministries of education and related educational authorities.
· Provide a basis for the objective assessment of the state of teaching and learning in a school, including staff and student performance by supervisors and inspectors.
· Provide information for the school community, the general public employers as well as educational and social science researchers for the advancement of knowledge.
· Enable school heads to collate information on pupils and staff for decision making by higher authorities, the law courts security agencies and other related government agencies when occasion demands.
· Provide a mechanism such as the school timetable for the productive management of time and coordination of school work and activities.
· Serve as data bank on which both the school head and staff and even students can draw on.
Potential of ICT in
Record Keeping
The usefulness of keeping school records with Information and Communication
Technologies (ICT) is for the following reasons:
Administrative Efficiency: One major setback in achieving the
educational objective of the secondary education is inefficiency of the
principal in keeping some records. With the introduction of information and
communication technologies such as computers, digital libraries, e-mail,
internet and so on where information are stored and disseminated, principals
can do better in keeping records, and become effective and efficient in
performing their prescribed roles as administrators.
Availability of Information: Information and Communication Technologies will help maintain adequate and accurate records in our schools and make it available with ease.
Easy Retrieval: It also leads to easy accessibility and dissemination of information on school records, will become available for national planning, financial budgeting, effective implementation of the educational programs and policies.
School record keeping is all about information collection, storage, retrieval, use, transmission, manipulation and dissemination for the purpose of enriching communication, decision-making and problem solving ability in the school system. It is therefore necessary that this process be as accurate and accessible as possible. Using ICT in keeping school records will help to facilitate and enhance the administration of the school towards achieving the goals of the secondary education.
Scope of ICT in bringing inclusion in classrooms
A teacher must thrive to bring inclusion inside the classrooms as he is the one who directly deals with the diversities inside classrooms. In attempt to attain this goal, ICT should be adopted in the teacher education programs. This can be done to meet the following purposes: ˆ
· For imparting basic skills of computers. ˆ
· For enhancing communication in learning. ˆ
· For fostering self-learning. ˆ
· For helping the working teachers to update their knowledge base with respect to trending and new technologies from time to time. ˆ
· For removing communication, cultural and geographical barriers. ˆ
· For assisting and enhancing the evaluation, assessment and feedback mechanism. ˆ
· To foster cooperative learning and team teaching by collaborating teachers together. ˆ
· For making interactive phase of teaching more interesting. ˆ
· For aiding teachers in their pre-active phase of teaching. ˆ
· For providing accessibility in distance learning.
Any tool or service that is helpful in advancing student learning. An evidence-based applied science derived from basic educational and psychological research enhances capabilities of exploring ideas, innovations and communication.
Examples of some AT to help PWDs in education includes: ˆ
· Braille Duplicators and Writers ˆ
· Group Hearing Aid for classrooms ˆ
· Alternative & Augmentative Communication software/devices ˆ
· Multi-Sensory systems ˆ
· Tactile mathematical devices ˆ
· Tactile geography devices ˆ
· Tactile science devices ˆ
· Screen readers & magnifiers ˆ
· Assessment & evaluation tool ˆ
· Models ˆ
· Multimedia Content ˆ
· Content Development Software ˆ
· Word Bank & Prediction Systems ˆ
· Text-to-Speech Engines & Speech Recognition ˆ
· Special Access Switches & Mechanism ˆ
· Sign Language & Braille Learning Software etc. ˆ
· Web-Portal ˆ
· Edusat ˆ
· M-Learning ˆ
· Web-cast ˆ
· Online learning ˆ
· On demand examination
Benefits of ICT
Some of the claimed benefits of ICT for Education are: ˆ
Easy-to-access Course Material – Multimedia/ easy to understand course material can be posted on web which learners can access at a time and location they prefer ˆ
Motivation - Computer-based instruction can give instant feedback to students and explain correct answers. Moreover, a computer is patient and non-judgmental, which can give the student motivation to continue learning ˆ
Wide Participation - Learning material can be used for long distance learning and are accessible to a wider audience ˆ
Improved student writing - Convenient for students to edit their written work which can, in turn, improve the quality of their writing ˆ
Subjects made easier to learn - Many different types of educational software are designed and developed to help
It is imperative for a teacher to have the necessary knowledge and skills required for removal of common learning barriers that arise due to the individual differences of cultural, social, physical, psychological and economic nature in classrooms and to ensure that the classroom is truly inclusive in nature. The paper has attempted to acquaint the teacher educators with the tools of ICT along with their benefits and applications in Indian classrooms so that they train the pre-service teachers and in-service teachers to use them and apply for effective learning of students.