Unit 4: Technology Facilitating Education
4.1 Technology and its impact on education: Changing Trends in teaching & learning
4.2 Technology products for educational purposes: Listening (Induction loop/FM/IR), Visual (Speech to text/text to speech) Audio-Visual (computer based learning & self learning packages, Multimedia)
4.3 Technology Based Educational Services: Online learning, Web based learning, Computer assisted Learning, Video remote interpreting, C-Print technology, Open, Close and Real time Captioning
4.4 ICT and education of children with Hearing Impairment: Planning, Implementation & Evaluation of teaching-learning
4.5 Future technologies: Universal Design: Meaning & Scope
4.1 Technology and its impact on education: Changing Trends in teaching & learning
Technology has had a significant positive impact on education in recent years. With the proliferation of the internet and the widespread adoption of devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones, students and teachers now have access to a wealth of information and resources that were previously unavailable. One major benefit of technology in education is the ability for students to access information and resources anytime, anywhere. With the internet at their fingertips, students can now easily find the answers to their questions and complete assignments from the comfort of their own homes. This flexibility allows students to learn at their own pace and gives them the freedom to choose when and where they learn. Another positive impact of technology on education is the ability to personalize learning. With the use of adaptive learning software, teachers can now create customized lesson plans and assignments based on the individual needs and abilities of their students. This personalized approach to education can help students feel more engaged and motivated to learn, as they are able to focus on the topics and skills that are most relevant to their needs. Technology has also made it easier for teachers to collaborate and share resources with their colleagues. Through the use of online platforms and social media, teachers can connect with each other and share lesson plans, activities, and other teaching materials. This collaboration helps teachers stay up-to-date on the latest teaching techniques and can also save them time and effort when it comes to creating their own lesson plans.
All of us, together, are surging through the most profound revolution in human history. Its impact is personal, national, global and in many ways, unlimited. Yes, it is the impact of technology. This new networked age makes it urgent to rethink entirely what we mean by education, learning, teaching and schooling. For education is changing more than it has since the invention of the printing press over 500 years ago, as now the world is your classroom and learning is lifelong. Already two billion students spend four-fifths of their working hours outside school, in an iPod, YouTube, Google, Wikipedia, etc.
It’s Personal: where information and learning programs can be personalized. And you can share your own talents and skills with millions- for both fun and income.
It’s Interactive: with new digital platforms and templates to make it easy, simple and fun to learn by doing, creating and interacting- a new world of creative experiences.
It’s Global: the ever-expanding worldwide internet, owned by none, used by everyone; where the combined knowledge of humankind is now available to virtually all at the tap of a digital keyboard or a touch screen.
It’s mainly free: or nearly so, one low-cost click at a time. The World Wide Web, browsers, search engines and digital platforms make it easy to access much information free.
Impacts of technology on Education are the following:
Easy access to information; easy retention of information, more storage of information, better presentation of information, teaching became more interactive, easy sharing of knowledge and more interest in learning.
The
field of education (teaching and learning) has revolutionized since the advent
of technology. Schools have realized the importance of technology and have
started implementing it in the classrooms. With the arrival of computers in
schools, it has become easier for teachers to impart knowledge and for the
students to acquire it. The onset of technology has made the journey of
teaching and learning more effective.
Technology is a teaching
tool
Computers provide us with an interactive audio-visual medium. Animation software and Power Point presentations are used to present information in an interactive way. Both teachers and students find it helpful and interesting to use audio-visual tools. Large number of students can be addressed simultaneously with the help of projectors, screens, microphones and speakers. These teaching aids have led to increased attendance in classes.
Technology has made student life easy
Technology has made the life of students easier. Nowadays, students use different software and tools to make presentations and projects, instead of using pen and paper. An iPad is very light as compared to a pile of notebooks. Surfing an E book is easier as compared to a heavy book. These tools help to generate more interest in studies. There are online libraries which require no physical space. The teachers, students and researchers sitting in different parts of the world can access the same online library simultaneously.
Sharpening students’ critical thinking
Technology will have an impact on students’ critical thinking skills depending on a variety of elements, including the type of technology used and the context in which it is used.
It is a well-known fact that the use of technology in the classroom can make activities and the learning process more engaging. Technology has the ability to engage multiple senses and can increase students’ investment in the material.
Appropriate classroom technology boosts students’ academic achievement, self-confidence, motivation in class, and attendance. Technology facilitates students’ transition from sitting attentively and listening to more hands-on learning.
In addition, technology influences critical thinking by assisting students in applying what they’ve learned to real-life situations and developing problem-solving skills, both of which are essential components of critical thinking.
Easy to store information
Due to technology, data storage has become much easier. It takes few seconds to type or copy-paste various information. A small pen drive can store huge amount of information. So, managing records online is easier. Computers enable better and strong storage of data as compared to managing hard copies.
Digital classrooms
Both students and teachers get benefited through the use of digitized boards in classrooms. Thanks to the advanced technology that we can see the entire syllabus online and then decide which courses and subjects we should opt for. Interactive digitized boards can be used by students for drawing figures, making diagrams, doing mathematical calculations, etc.
Information is easily accessible
The internet search engines are a source of immense information. They are now used as an effective tool for searching information. All this is possible in just one or two clicks. Both teachers and students are benefited through this.
Wikipedia is the ideal example, around ten years ago, it didn’t even exist. Now, it is by far the world’s largest encyclopedia. It has around 2.5 million entries: instantly available free, on the Web. All are contributed free by more than 75,000 volunteers. Wikipedia provides an excellent platform for cooperative sharing.
Teaching is sharing
The application of technology has made education more collaborative. There are online forums where subject experts can meet and discuss subject specific topics, review the syllabus and plan assessments to enhance the process of teaching. Teachers can impart customized education to cater different learning abilities and needs of the students. Everyone has a personal learning style, almost as unique as one’s fingerprints. Any skills can now be taught online in sequence, from beginner level to master level. Good teachers and multimedia experts can tailor such instant learning programs to individual learning styles and in individual modules.
Technology has removed space and time limitations
There are different online education programs available which has given a new dimension to education. The students and teachers can be a part of one virtual classroom, even if they are physically far away from each other. Some universities offer online educational programs where students and teachers can interact with each other through internet. There are online libraries with books, journals, encyclopedias, etc. where students can access various resources, highlight, save and use the soft copies.
Increased collaboration
Collaboration can be aided by educational technology. Teachers can communicate with students during lessons, but students can also interact with one another. Students collaborate to solve problems through online classes and educational games.
Students can share their ideas and thoughts and encourage one another in collaborative activities. Simultaneously, technology allows for one-on-one interaction with teachers. Students can ask questions about the classroom and receive additional assistance with the difficult-to-understand subject matter. Students can upload homework from home, and teachers can access and view submitted assignments on their devices.
The education sector has been long overdue to adopt technology trends. The latest educational technology trends are a refreshing change. Since the pandemic transitioned learning from the classroom to homes, we have witnessed new ways of educating.
Innovative trends in educational technology provide opportunities to fulfill growing education needs. Solutions like online classes provide a way to keep classes going, and trends like augmented reality and immersive learning are fundamental to leverage growth and elevate the learning experience.
Since the pandemic made distance learning necessary, it presented a unique opportunity to adopt digital trends that can adapt and carry over to in-person instruction. The emerging trends in educational technology focus on connectivity, versatility and student-centered learning.
Social Media in Learning
Who would have ever thought that social media would one day be accepted as part of the learning process? The technological trends in teaching and learning are rapidly changing every day. With kids as young as eleven having social media profiles on various platforms, you can’t really expect to keep them away from social media for too long. So, teachers found a way to utilize this trend and turn it into a powerful tool for enhancing the learning process.
Educational institutes have started using social media as a communication tool, where students can interact with their peers and faculty members. Usually, students share videos and images with their friends and followers. But with social features embedded in their eBooks, they can share study materials, opinions, projects etc.
They can comment on someone else’s post or share links to other websites, all the while building peer networks and enhancing the online learning experience. Teachers allow the use of social media as part of the learning model because it helps students to stay interested in their course and increases engagement. Social media is here to stay and incorporating it into learning modules will build a culture of collaboration and sharing, leading to an improved learning experience.
Immersive Learning with AR and VR
With the introduction of augmented reality and virtual reality into the education system, the classroom learning experience has undergone a tremendous change. Learning has become much more immersive than traditional methods. Unlike plain images and hands-on experiments in the lab, students can now view enhanced versions of the image and objects on their mobile devices. The augmented and virtual reality trends in education technology are making learning a compelling experience.
While augmented reality provides an enhanced view of a real image, virtual reality gives a false perception of reality around them. Both these techniques have taken digital learning to new dimensions. AR and VR are increasingly being used to explain complex concepts. From atoms to planets, and from Egypt to the Colosseum, students can explore and learn so much more.
Gamification in Education
The latest trends in educational technology have been gaining popularity for the simple reason that it increases student engagement. We have seen gamification being used in classrooms in different forms such as leaderboards, reward points, badges, stickers etc. Of all the trends in education technology, gamification is the one trend which guarantees an increase in participation, engagement, and competition.
Students become actively involved in the classroom activities to increase their scores and leaderboard rankings. And the need to lead the scoreboards result in improved performance and better retention.
Gamification incentivizes students to learn and practice, improving the overall learning process. So, teachers use gamification as a means to increase engagement, boost motivation and create an interactive classroom environment.
Either ways, it is helpful in increasing students’ morale and encourages them to perform better every time. We can see this trend being utilized further, in more innovative ways to enhance the learning model.
Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous online learning gives students more flexibility and freedom during the school day. It allows students to set their preferred learning schedule within a given timeframe. Students can view instructional information and materials at any time during the week as long as they complete their required assignments and tasks. Asynchronous learning empowers students to take a hands-on role in their education and practice self-sufficiency and time management skills. Online learning makes this possible because it allows students to view materials from any location.
Today’s digital learning offers everything students and teachers need readily at their fingertips in advanced designs. Modern technology used in schools provides an environmentally friendly approach with less paper waste. Organize your classroom with these beneficial systems:
1. Projectors: Notes, images or presentations project onto any flat surface.
2. Smartboards: A digitized recording captures written content on a board with digital or real markers.
3. Laptops and tablets: Electronic portable devices offer note-taking and learning activity opportunities.
4. PowerGistics Towers: A vertical Tower charges and stores laptops, Chromebooks, tablets, iPads and mobile devices.
5. Ultra-High-Definition Television: Educational movies and videos display on wide-screen TVs.
Technology has dramatically advanced, and this has had a significant good and bad effect on how education is offered. Teachers’ teaching practices have evolved in tandem with the constant advancement of technology. Technology has maximized what and how quickly a student can learn and also save a lot of time on training or even on assignments, for example, you can very easily buy personal statement online.. Nevertheless, just as inappropriate use of anything may have a negative consequence, so can the wrong use of technology.
4.2 Technology products for educational purposes: Listening (Induction loop/FM/IR), Visual (Speech to text/text to speech) Audio-Visual (computer based learning & self learning packages, Multimedia)
Listening (Induction loop/FM/IR)
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) are personal technologies that can help you communicate in one-to-one conversations. They are hand-held amplifiers with microphones that bring the sound you wish to hear closer to your ears. These small devices capture the sound you want to hear and may filter some background noise. A Pocketalker is an inexpensive, wired, example of this type of device. There are other personal devices, such as wireless FM devices and propriety devices that are sold by audiologists as ancillary equipment to various brands of hearing aids and cochlear implants.
An assistive listening device (ALD) is part of a system used to improve hearing ability for people in a variety of situations where they are unable to distinguish speech in noisy environments. Often, in a noisy or crowded room it is almost impossible for an individual who is hard of hearing to distinguish one voice among many. This is often exacerbated by the effect of room acoustics on the quality of perceived speech. Hearing aids are able to amplify and process these sounds, and improve the speech to noise ratio. However, if the sound is too distorted by the time it reaches the listener, even the best hearing aids will struggle to unscramble the signal. Assistive listening devices offer a more adaptive alternative to hearing aids, but can be more complex and cumbersome.
Assistive listening systems (ALSs) generally refers to system-wide technology that's useful in public settings such as a theater, airport, church or lecture hall. The Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA, mandates that most public places offer some type of assistive listening system.
There are three types of ALSs recognized by the ADA:
- Hearing loops, also known as induction loops or audio frequency induction loop systems (AFILS), consist of a copper wire placed within a room, theater, or counter that is connected via a special loop “driver” to a public address or sound system. Sound is wirelessly transmitted via small changes in the magnetic field and is directed into the telecoil of hearing aids, cochlear implants, or telecoil receivers worn on the body, like a neckloop.
- FM or DM systems, or radio frequency assistive listening systems, transmit wireless, low-power FM frequency radio transmission from a sound system to FM receivers. Everyone using the system needs a receiver and either headphones or a neckoop. For those who have telecoil-equipped hearing aids, neckloops eliminate the need for headphones. These systems are widely used in schools to help children with hearing loss achieve their educational goals but they are also helpful for adults in many situations.
- Infrared systems (IR) use invisible infrared light waves to transmit speech or music from a public address or sound system to an IR receiver. This technology is line-of-sight and can't be used in direct sunlight. Because IR signals are sent and received in a straight line, users are encouraged to sit as centrally as possible.
All assistive listening systems are required to be accessible for people with hearing aids, hearing aids with a telecoil, or hearing aids with no telecoil.
Hearing aid technology is impressive and can be a big help for people with hearing loss. However, if you have unique needs that aren’t addressed by your hearing aids or if you aren’t yet ready for hearing aids, assistive listening devices or systems can be the answer.
Visual (Speech to text/text to speech)
Text-to-speech (TTS) is a type of assistive technology that reads digital text aloud. It’s sometimes called “read aloud” technology.
Text-to-speech technology is software that takes text as an input and produces audible speech as an output. In other words, it goes from text to speech, making TTS one of the more aptly named technologies of the digital revolution. A TTS system includes the software that predicts the best possible pronunciation of any given text. It also bundles in the program that produces voice sound waves; that’s called a vocoder.
TTS works with nearly every personal digital device, including computers, smartphones and tablets. All kinds of text files can be read aloud, including Word and Pages documents. Even online web pages can be read aloud.
The voice in TTS is computer-generated, and reading speed can usually be sped up or slowed down. Voice quality varies, but some voices sound human. There are even computer-generated voices that sound like children speaking.
Many TTS tools highlight words as they are read aloud. This allows kids to see text and hear it at the same time.
Some TTS tools also have a technology called optical character recognition (OCR). OCR allows TTS tools to read text aloud from images. For example, your child could take a photo of a street sign and have the words on the sign turned into audio.
Types of text-to-speech tools
Depending on the device your child uses, there are many different TTS tools:
- Built-in text-to-speech: Many devices have built-in TTS tools. This includes desktop and laptop computers, smartphones and digital tablets and Chrome. Your child can use this TTS without purchasing special apps or software.
- Web-based tools: Some websites have TTS tools on-site. For instance, you can turn on our website’s “Reading Assist” tool, located in the lower left corner of your screen, to have this webpage read aloud. Also, kids with dyslexia may qualify for a free Bookshare account with digital books that can be read with TTS. There are also free TTS tools available online.
- Text-to-speech apps: Kids can also download TTS apps on smartphones and digital tablets. These apps often have special features like text highlighting in different colors and OCR. Some examples include Voice Dream Reader, Claro ScanPen and Office Lens.
- Chrome tools: Chrome is a relatively new platform with several TTS tools. These include Read&Write for Google Chrome and Snap&Read Universal. You can use these tools on a Chromebook or any computer with the Chrome browser. See more Chrome tools to help with reading.
- Text-to-speech software programs: There are also several literacy software programs for desktop and laptop computers. In addition to other reading and writing tools, many of these programs have TTS. Examples include Kurzweil 3000, ClaroRead and Read&Write. Microsoft’s Immersive Reader tool also has TTS. It can be found in programs like OneNote and Word. See more examples of software for kids with reading issues.
Text-to-speech technology converts text on a screen and reads it out loud to you. This can be helpful to you in a few ways:
- It can improve your literacy skills, including word recognition, definitions, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
- It's great for proofreading papers! Listening to your written work being read out loud helps you catch grammatical and spelling mistakes.
- It's great for reading research articles! Use text-to-speech to read articles out loud to you. Research shows that listening to information can help with comprehension and recall.
Text-to-speech can be used with:
- PDFs
- Microsoft Word documents
- Emails
- Web pages
- and more!
Speech recognition, or speech-to-text, software is designed to transcribe spoken language into text. These tools are also useful for individuals with struggle with organizing their thoughts and getting them out on paper so to speak. STT tools make it easy to simply dictate your notes, discussion posts, papers, etc.
Speech to Text tools are available on your computer through your device, browser or extensions. This technology premiered in 1936 with the first text to speech device and over time continued to develop with more advanced and improved technology. Speech technology installed on computers or devices with different apps and software help anyone with dyslexia or other learning disabilities.
Today speech technology is everywhere and can recognize spoken words and convert them to text. We interact with speech recognition tools when we call companies with automated customer service. Voice assistants can reply with accuracy in response to answers supplied by the caller.
Currently, all major technology companies have invested heavily in the development of speech recognition. Amazon Alexa, Apple Siri, and Google Home are used in homes and speech recognition which can control devices in smart homes. Speech recognition is also used in cars with navigation, making cell phone calls and getting information on restaurants, movie theaters, and stores.
Text to Speech Browser Extensions
There are speech to text tools and extensions on your computer and devices that will also give you the ability to speak and it will type in your words. If you are wanting to read back your words enable TTS or Text to Speech, Installing the appropriate extension will enable you to highlight the text you want to read and choose to speak on your extension like chrome browsers or google chrome .
Instructional Use
- Students can use accessibility settings, software, or other tools as an alternative to writing or typing in order to produce work that requires textual responses.
- Students use audio-recording devices or scribes as alternatives to writing when a processing or physical challenge is present. A trained adult may then transcribe the student’s response word-for-word on the student’s test or assignment.
- For students with motor skill limitations, physical disabilities, blindness/low vision, or other difficulties accessing a standard keyboard and mouse, voice dictation may be beneficial.
- By removing the physical barriers to writing and navigation of the computer, student’s access to technology and classroom activities can be increased.
- Teachers use speech recognition technology for students to encourage writing that is more thoughtful and deliberate.
- Students dictate their responses to instructional tasks to each other and check the written content for correctness utilizing speech-to-text.
Audio-Visual (computer based learning & self learning packages, Multimedia)
The computer has become an accepted teaching resource within most subjects taught in the curriculum. Combined with other audio-visual techniques the resultant integrated multimedia approach to the presentation of pedagogical information can provide teaching strategies hitherto not available via conventional teaching methodologies.
In modern world we use digital tools to improve the teaching-learning process. The most common tool we use in classroom these days is PowerPoint slides, which makes the class more interesting, dynamic and effective. Moreover it also helps to introduce new topics in easy way. The use of audiovisual aids makes the students to remember the concept for longer period of time. They convey the same meaning as words but it gives clear concepts thus help to bring effectiveness in learning.
Integrating technology into the classroom help students to experience things virtually or vicariously. For example, if the teacher wants to give a lesson on Taj Mahal, it is possible that not all the students in India have visited the place but you can show it through a video thereby allowing the students to see the monument with their own eyes. Although the first hand experience is the best way of educative experience but such an experience cannot always be done practical so in some case we need to have substitution.
Use of audio-visual aids help in maintaining discipline in the class since all the students' attention are focused in learning. This interactive session also develops critical thinking and reasoning that are important components of the teaching-learning process.
Audiovisual provides opportunities for effective communication between teacher and students in learning. For example, in a study on English as Foreign Language (EFL) classroom, the difficulties faced by EFL learner are lack of motivation, lack of exposure to the target language and lack of pronunciation by teacher, and such difficulties can be overcome by Audio as purpose of communication and Visual as more exposure.
Students learn when they are motivated and curious about something. Traditional verbal instructions can be boring and painful for students. However, use of audio-visual provides intrinsic motivation to students by peaking their curiosity and stimulating their interests in the subjects.
It is clear that audio visual aids are important tools for teaching learning process. It helps the teacher to present the lesson effectively and students learn and retain the concepts better and for longer duration. Use of audio visual aids improves student's critical and analytical thinking. It helps to remove abstract concepts through visual presentation. However, improper and unplanned use of these aids can have negative effect on the learning outcome. Therefore, teachers should be well trained through in-service training to maximize the benefits of using these aids. The curriculum should be designed such that there are options to activity based learning through audio-visual aids. In addition, government should fund resources to purchase audio-visual aids in schools.
4.3 Technology Based Educational Services: Online learning, Web based learning, Computer assisted Learning, Video remote interpreting, C-Print technology, Open, Close and Real time Captioning
Online learning
One of the most oft-used terms after the pandemic is the term “new normal.” The new normal in education is the increased use of online learning tools. The COVID-19 pandemic has triggered new ways of learning. All around the world, educational institutions are looking toward online learning platforms to continue with the process of educating students. The new normal now is a transformed concept of education with online learning at the core of this transformation. Today, digital learning has emerged as a necessary resource for students and schools all over the world. For many educational institutes, this is an entirely new way of education that they have had to adopt. Online learning is now applicable not just to learn academics but it also extends to learning extracurricular activities for students as well. In recent months, the demand for online learning has risen significantly, and it will continue doing so in the future.
As with most teaching methods, online learning also has its own set of positives and negatives. Decoding and understanding these positives and negatives will help institutes in creating strategies for more efficiently delivering the lessons, ensuring an uninterrupted learning journey for students.
Advantages Of Online Learning
1. Efficiency
Online learning offers teachers an efficient way to deliver lessons to students. Online learning has a number of tools such as videos, PDFs, podcasts, and teachers can use all these tools as part of their lesson plans. By extending the lesson plan beyond traditional textbooks to include online resources, teachers are able to become more efficient educators.
2. Accessibility Of Time And Place
Another advantage of online education is that it allows students to attend classes from any location of their choice. It also allows schools to reach out to a more extensive network of students, instead of being restricted by geographical boundaries. Additionally, online lectures can be recorded, archived, and shared for future reference. This allows students to access the learning material at a time of their comfort.
Thus, online learning offers students the accessibility of time and place in education.
3. Affordability
Another advantage of online learning is reduced financial costs. Online education is far more affordable as compared to physical learning. This is because online learning eliminates the cost points of student transportation, student meals, and most importantly, real estate. Additionally, all the course or study materials are available online, thus creating a paperless learning environment which is more affordable, while also being beneficial to the environment.
4. Improved Student Attendance
Since online classes can be taken from home or location of choice, there are fewer chances of students missing out on lessons.
5. Suits A Variety Of Learning Styles
Every student has a different learning journey and a different learning style. Some students are visual learners, while some students prefer to learn through audio. Similarly, some students thrive in the classroom, and other students are solo learners who get distracted by large groups.
The online learning system, with its range of options and resources, can be personalized in many ways. It is the best way to create a perfect learning environment suited to the needs of each student.
Disadvantages Of Online Learning
1. Inability To Focus On Screens
For many students, one of the biggest challenges of online learning is the struggle with focusing on the screen for long periods of time. With online learning, there is also a greater chance for students to be easily distracted by social media or other sites. Therefore, it is imperative for the teachers to keep their online classes crisp, engaging, and interactive to help students stay focused on the lesson.
2. Technology Issues
Another key challenge of online classes is internet connectivity. While internet penetration has grown in leaps and bounds over the past few years, in smaller cities and towns, a consistent connection with decent speed is a problem. Without a consistent internet connection for students or teachers, there can be a lack of continuity in learning for the child. This is detrimental to the education process.
3. Sense Of Isolation
Students can learn a lot from being in the company of their peers. However, in an online class, there are minimal physical interactions between students and teachers. This often results in a sense of isolation for the students. In this situation, it is imperative that the school allow for other forms of communication between the students, peers, and teachers. This can include online messages, emails and video conferencing that will allow for face-to-face interaction and reduce the sense of isolation.
4. Teacher Training
Online learning requires teachers to have a basic understanding of using digital forms of learning. However, this is not the case always. Very often, teachers have a very basic understanding of technology. Sometimes, they don’t even have the necessary resources and tools to conducts online classes.
To combat this, it is important for schools to invest in training teachers with the latest technology updates so that they can conduct their online classes seamlessly.
5. Manage Screen Time
Many parents are concerned about the health hazards of having their children spend so many hours staring at a screen. This increase in screen time is one of the biggest concerns and disadvantages of online learning. Sometimes students also develop bad posture and other physical problems due to staying hunched in front of a screen.
Web based learning
Web-based learning refers to the type of learning that uses the Internet as an instructional delivery tool to carry out various learning activities. It can take the form of
(1) a pure online learning in which the curriculum and learning are implemented online without face-to-face meeting between the instructor and the students, or
(2) a hybrid in which the instructor meets the students half of the time online and half of the time in the classroom, depending on the needs and requirement of the curriculum.
Web-based learning can be integrated into a curriculum that turns into a full-blown course or as a supplement to traditional courses.
Web based learning is often called online learning or e-learning because it includes online course content. Discussion forums via email, videoconferencing, and live lectures (video streaming) are all possible through the web. Web based courses may also provide static pages such as printed course materials. One of the values of using the web to access course materials is that web pages may contain hyperlinks to other parts of the web, thus enabling access to a vast amount of web based information.
Advantages Of Web Based Learning
1. You are able to link the various resources in several varying formats.
2. It is a very efficient way of delivering courses online.
3. Due to its convenience and flexibility, the resources are available from anywhere and at any time.
4. Everyone, who are part time students or are working full time, can take advantage of web-based learning.
5. Web-based learning promotes active and independent learning.
6. As you have access to the net 24x7, you can train yourself anytime and from anywhere also.
7. It is a very convenient and flexible option; above all, you don't have to depend on anyone for anything.
8. Not only can you train yourself on a day to day basis, but also on weekends or whenever you have the free time to. There is no hard and fast rule.
9. Through discussion boards and chats, you are able to interact with everyone online and also clear your doubts if any.
10.The video instructions that are provided for audio and video learning can be rewound and seen and heard again and again if you do not happen to understand the topic first time around.
Disadvantages Of Web Based Learning
Well, there are not many disadvantages of eLearning, the main one being that you get knowledge only on a theoretical basis and when it comes to putting to use whatever you have learnt, it may be a little different. The face-to-face learning experience is missing, which may matter to some of you.
1. Most of the online assessments are limited to questions that are only objective in nature.
2. There is also the problem of the extent of security of online learning programs.
3. The authenticity of a particular student's work is also a problem as online just about anyone can do a project rather than the actual student itself.
4. The assessments that are computer marked generally have a tendency of being only knowledge-based and not necessarily practicality-based.
Computer assisted Learning
Computer-assisted
learning (CAL) Any use of computers to aid or support the
education or training of people. CAL can test attainment at any point, provide
faster or slower routes through the material for people of different aptitudes,
and can maintain a progress record for the instructor.
Computer-assisted
learning is one of several terms used to describe this application of
computers. Other terms include computer-aided (or-
assisted) instruction, CAI, computer-based learning, CBL,
and computer-managed instruction, CMI.
Computer-assisted learning describes the education that uses computers and other technologies and doesn’t require human intervention or interaction. It can take many different forms, as we’ll review below, and, despite its name, it involves a range of tools and devices, such as mobile devices, tablets, desktops, and others.
CAL incorporates different types of software and methodologies. It can be applied to a wide range of subjects, from language learning to math. It’s also used across education levels, including K-12, higher education, and adult courses.
Types of CAL
• Tutorials
Tutorial software provides information about diverse topics, essentially taking on the role of the instructor. In many cases, the technology quizzes and evaluates the student’s comprehension of the subject matter using an interactive process and delivering feedback.
• Gamified Learning
This type of CAL uses a gamified approach to help students learn the material. Through an interactive process, students may advance to new levels after demonstrating that they’ve grasped certain concepts or receive rewards along the way.
• Practice
Practice technology applies a digital approach to traditional methods of learning content, such as flashcards. The technology, for example, might quiz learners on different concepts.
• Demonstrations
Demonstrations tap into different senses, like visual and auditory, to present facts, information, concepts, and more. In some cases, students can become “immersed” in the experience, as is often the case with virtual or augmented reality technologies, both of which are used in teaching and learning.
Pros of Computer-Assisted Learning
1. Students and Instructors Can Receive Real-Time Feedback
CAL reveals solutions and assesses student performance immediately. Therefore, it can deliver immediate feedback to the learner, not only cataloging mistakes but also providing analytics that go a step beyond to help students improve. This is also beneficial for instructors, who can use this data as a tool to inform their own teaching and as well as their assessment of student performance.
2. The Learning Process Is More Interactive and Engaging
CAL takes on many different forms, and each one is meant to engage learners. Students are likely to respond to these new, exciting ways of gaining exposure to and absorbing content — often far more so than learning through traditional classroom instruction. Because there are so many different methods associated with CAL, the risk of boredom is greatly reduced.
CAL is usually interactive, too, which involves students and makes them agents of their own learning, increasing their stake in the education process.
3. Learning Can Be More Personalized
Many CAL programs adjust the approaches based on the individual learner’s progress. The software adapts according to how the student is learning, whether it’s a game, interactive demonstration, or assessment. Students can also go at a pace that works for them, and the program will adjust to meet them where they are.
A more personalized approach leads to both a higher level of engagement and stronger learning outcomes.
4. Technology Can Fill the Gaps for Students with Learning Differences
CAL has implications for students with a range of learning differences, too, giving greater access to those with different educational and learning needs. Because accessibility is such an important concern, CAL’s relevance is underscored in this arena. Through a personalized, adjustable approach, CAL tools can address a range of special needs.
Cons of Computer-Assisted Learning
1. CAL Can Become a Distraction
When students use CAL tools in the classroom, they may well have trouble focusing on the live teaching taking place. Getting students to pay attention is a constant complaint from instructors who teach at all levels, and when technology enters the picture, it’s even easier for students to get distracted.
2. It’s Expensive
In many cases, technology is expensive. CAL solutions may be difficult to purchase and implement because of the cost barrier associated with them. This is especially true when the tools are custom-built for a particular audience, although educators should keep in mind that there are some more cost-effective solutions.
3. Software Can Become Outdated Quickly
With frequent advances in technology and reassessments and reconceptualizations of material and content, there is a risk of applying technologies that could be irrelevant or outdated quickly. Given the high cost associated with CAL, educators who are considering implementing these tools should research solutions or work closely with developers to ensure that the technology can be altered to incorporate new content.
4. There’s a Risk of Over-Dependence on the Technology
CAL should augment instructor efforts, not replace them. While there are some contexts in which technology may play a greater role — for example, if an adult learner is attempting to learn a language on their own through a platform like Duolingo —, the tools and live instruction often go hand in hand. With CAL, there is a risk of both instructors and students becoming over-reliant on the technology to do the legwork.
Moreover, some teachers may feel that they have trouble finding tools that meet their lesson plan needs and attempt to alter their lessons accordingly, when the reverse should be true — they should find technologies that enhance and support their lesson plans.
In the best-case scenario, computer-assisted learning benefits and enhances instruction. But that doesn’t mean that it’s without its flaws. Ideally, instructors will find a balance between using technology to improve and supplement their own teaching, supporting both learners and teachers in education.
Video remote interpreting
Video remote interpreting (VRI) is a form of sign language interpreting that allows people who are deaf or hard of hearing to communicate with a hearing person at the same site via videoconferencing instead of live, on-site interpreting. VRI is especially useful when (1) there is a lack of available qualified interpreters, such as at a rural location; and (2) when an interpreter is needed immediately and there is no available interpreter on-site.
VRI works by using videoconferencing equipment at both locations. The interpreter, who is typically at a call center, uses a headset to hear what the hearing person says. As the hearing person speaks, the interpreter signs everything said to a web camera. When the person who is deaf replies via their web camera, the interpreter sees and voices the interpretation. The person who is deaf and the person who is hearing can talk back and forth, just as if the interpreter was in the same room.
VRI is provided on a fee-for-service basis by several interpreting agencies; costs may vary based on whether an interpreter is needed immediately or is scheduled ahead of time.
More information on VRI can be provided by a local sign language interpreting agency, which can be found by searching for "video remote interpreting" on the web.
The Pros of VRI
Instant – With the touch of a button to a VRI service, one can have an interpreter there to translate from visual language to spoken language and vice versa. These services are available 24 hours a day and are often available on-demand. Many of these services also provide language translation services, so that nearly anyone that needs to is able to communicate instantly. One place where this need is extreme is in emergency rooms around the world. When someone arrives needing medical care, but they are deaf or hard-of-hearing, it can be a matter of life or death for them to be able to communicate with doctors and nurses about their condition.
Trained Professionals – VRI is done by trained professionals who are able to communicate well and thoroughly every time. Having content specialists in the translating role is important as well. Again, in an emergency medical situation, someone who knows medical terminology and is able to translate it well can be vital. Also, a trained professional will understand cultural differences and norms that need to be observed. When providing a service, one doesn’t want to offend a patient or client.
Unobtrusive – In the case of events like a business meeting, VRI can appear as simply another person in the meeting. The interpreter is there to translate what is said and then can speak whenever the deaf attendee needs to be able to communicate. Modern video technology would even allow them to have a tablet or smartphone with the interpreter on it so that their translation services are invisible to most of the attendees.
The Cons of VRI
Unstable Connections – In some locations, such as remote areas or in the heart of buildings, VRI might have an unstable signal. Disconnections can frustrate users. Because most connections occur over wifi, any steel that interrupts the signal might cause a disconnection. Unlike verbal translation, which is often conducted over an office landline, VRI’s video basis requires wifi and therefore is a susceptible signal interruption.
Visual Limitations – Sometimes persons that are deaf are also blind. VRI is not able to assist and can’t replace a live translator in these situations. Vision can also be limited when there is a large group that the translator needs to be able to see. If the person signing is a distance from the camera, it can be hard to see what they are signing well.
Distractions – In a busy emergency room or at a conference, there can be many different distractions in the background. While this can be planned for much of the time, when last-minute VRI is required, it might not be able to be helped. Visual and audible distractions can make communication more difficult.
C-Print technology
C-Print is a speech-to-text service that projects captions in real-time. By projecting speech-to-text in real-time, spoken communication is more accessible to individuals who are Deaf, experience hearing loss, or who have low vision.
C-Print may be used in:
- Educational settings
- Business meetings or conferences
- Medical appointments
- Classes and lectures
- Events and community gatherings
- Any setting where an individual or group requires the ability to read spoken communication
How does It Work?
- The C-Print captionist may provide services on-site or remotely.
- The C-Print captionist listens and simultaneously types lecture or meeting content into their specialized software, which produces a text version of the spoken information in real-time.
- This text can be projected on a screen, or computer or mobile device.
- C-Print is content-based (similar to a sign language interpreter) rather than verbatim (like a court reporter).
- C-Print is a concise and thorough translation of spoken English content. It includes as much of the conversation as possible, rather than a word-for-word transcription. It is easy to read and follow.
- After the presentation, a transcript may be provided (Braille transcripts are also available). This is an excellent way to compile study materials or create meeting minutes.
Open, Close and Real time Captioning
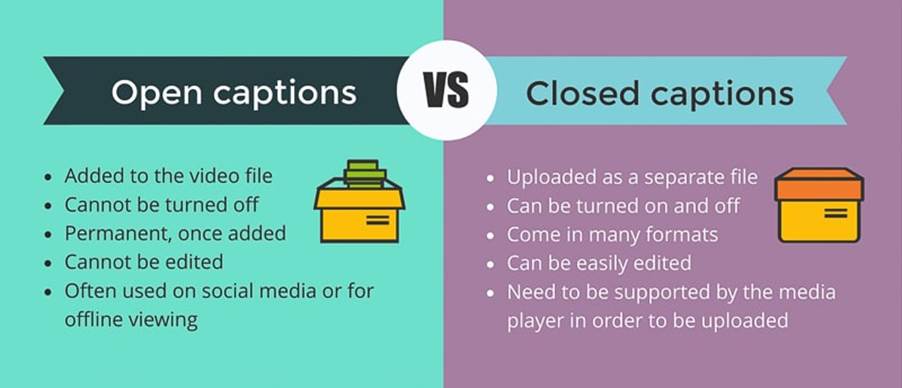
Video has played an important role in education for many decades. Now, in the form of computer-based multimedia, video is increasingly utilized in distance learning and other web-based educational applications. However, the audio portion of a video presentation is inaccessible to people who are deaf or hard of hearing unless it includes captions. Captions are on-screen text descriptions that display a video product's dialogue, identify speakers, and describe other relevant sounds that are otherwise inaccessible to people who are deaf or hard of hearing. Captions are synchronized with the video image so that viewers have equivalent access to the content that is originally presented in sound, regardless of whether they receive that content via audio or text. Captions are either open or closed. Open captions always are in view and cannot be turned off, whereas closed captions can be turned on and off by the viewer.
For video that is displayed on television sets, special devices called decoders must be available in order to view closed captions. Since 1993, decoders have been required to be built into television sets 13 inches or larger sold for use in the United States.
The meaning behind the term “closed captioning” is that captions are disabled by default. Users must activate the captions in order to view them, usually via remote control or by clicking a button. On YouTube, for example, the button reads “CC,” which stands for “closed captions.” Just as users can activate the captions, they can easily deactivate them by clicking the same button again. To dig deeper into what is closed captioning, let’s take a look at some examples, and review what organizations must take into account when they choose to provide viewers with this option.
Pros & Cons of Closed Captioning
As you can see, there are many pros to closed captioning, especially the fact that it’s there for those who need it, but isn’t intruding on the user experience for those who prefer to be without it. The ability to turn it on and off as needed provides the flexibility that empowers a customized, personalized experience.
Flexibility isn’t only for end-users. Closed captions are integrated into the video through an additional file, so if an error is found in the captions, but the video is fine, it’s much easier to fix. The mistake can be edited using closed captioning software or by a closed captioning service provider, without removing the video from the platform it’s been published on. That said, there are different types of closed captioning files, and not every device and media player supports them all. Even if they do, the captions’ fonts are determined by the player, meaning you cannot guarantee that it will look readable.
Another significant challenge is that people who are deaf or hard of hearing may feel excluded, or even miss some important information if captions are not activated right away, or if the font is not readable. And they’re not the only ones, as combining audio and text increases the learning impact for many people, even if they hear well. If a student isn’t used to using captions, it might not even occur to them to activate them, leading to potential loss.
Open captions are burned into the video, meaning they’re part of the video file just like the audio and the visuals, and viewers automatically see them. There is no way for viewers to turn them on or off.
The videos featured on Facebook are a prime example of open captioning. The videos are automatically muted, so the only way to fully understand the content without turning on the volume is by reading the captions. Similarly, if moviegoers watch a film in a foreign language and captions simply appear on their own on the TV or theater screen, that’s open captioning. If a video is set to be screened in front of a deaf or hard of hearing the audience, it is best to use open captioning to ensure everyone in the audience gets the most out of the content.
Pros & Cons of Open Captioning
It’s easy to see the difference between open and closed captions because the pros and cons are almost complete opposites. Primarily, choosing open captioning helps people who are hard of hearing feel equal. It is much more inclusive and beneficial to think about their needs in advance, instead of dealing with potential technical challenges at the beginning of the video, which might make them feel marginalized and less valuable to the course or university. That feeling can be worsened if the font isn’t very readable.
With open captioning, universities don’t need to worry about different types of closed captioning files, and whether or not they will work. Open captions are a part of the video file, and universities have control over visibility ahead of time. Professionals in the organization can review them and ensure everything works. Similarly, students don’t need to worry about it either. While activating closed captions might seem simple to those of us who work with technology on a regular basis, if students are not tech-savvy, universities need to work extra hard to ensure it’s not an effort for them to turn captions on.
It’s all about knowing your audience. If the majority of the students don’t need captions, and the captions end up hiding some important visuals, or there are students that get easily distracted by additional options, captions might end up interrupting the user experience. In this case, it might be best to present closed captions and work with a closed captioning software or service provider with proven experience, to ensure that those who need them have a seamless experience that doesn’t interrupt those who prefer uncaptioned content.
Real-time captions are created and displayed at the time of program origination. They are encased in white letters with a black background. They typically scroll up to three lines and the captions come after double chevrons ("greater than" symbols). The top line of the three lines disappears as a new bottom line is added, allowing the continuous rolling up of new lines of captions.
Real-time captioning is used for lectures/presentations, such as a training seminar, a corporate meeting, sporting events, or "live" events that do not allow time to prepare off-line captions. Real-time captioning simultaneously converts the spoken word into printed format using computer-aided translation, which appears on a large screen for anyone to view. The letters are similar to what one types on a computer screen.
4.4 ICT and education of children with Hearing Impairment: Planning, Implementation & Evaluation of teaching-learning
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is an extended term for information technology (IT) which stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals), computers as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage, and audio-visual systems, which enable users to access, store, transmit, and manipulate information.
The term ICT is also used to refer to the convergence of audio-visual and telephone networks with computer networks through a single cabling or link system. There are large economic incentives (huge cost savings due to elimination of the telephone network) to merge the telephone network with the computer network system using a single unified system of cabling, signal distribution and management.
However, ICT has no universal definition, as "the concepts, methods and applications involved in ICT are constantly evolving on an almost daily basis." The broadness of ICT covers any product that will store, retrieve, manipulate, transmit or receive information electronically in a digital form, e.g. personal computers, digital television, email, robots. Skills Framework for the Information Age is one of many models for describing and managing competencies for ICT professionals for the 21st century.
For the teacher, it is an initiation into:
· Learning to make right choices of hardware, software and ICT interactions
· Exploring educational possibilities of technology,
· Growing to become a critical user of ICT
For the student, it is an initiation into:
· Creativity and problem solving
· An introduction to the world of information and technologies
· An opportunity to shape career pursuits
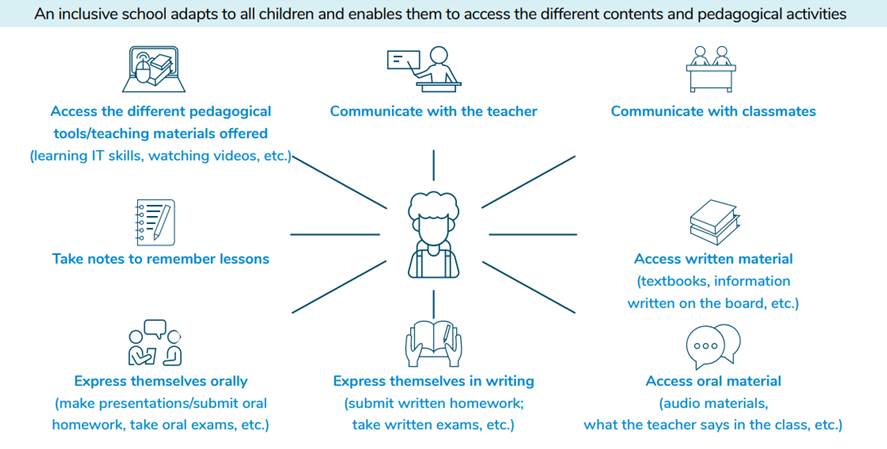
ICT has a key role to play in making schools places of knowledge, skills and attitudes free of any form of discrimination or segregation by providing teachers with a wide range of educational content and activities accessible to all their pupils. ICT can help learners to overcome difficulties in seeing, hearing, communicating, remembering/concentrating/learning or moving their upper limbs (a capacity often needed for writing or other school activities).
ICT can be divided into three main categories:
· The educational content and activities per se: digital media whose purpose is to transmit lessons/skills to the student (e.g. an audio book, an educational video with sign language interpretation, etc.).
· The hardware that serves as an intermediary to make certain educational content/activities accessible (e.g. a computer to view the sign language interpretation of an audio document; alternative communication software to facilitate communication with teachers).
· Accessibility features that make the hardware accessible to all (e.g. a screen reader that allows a student who is blind or visually impaired to use a computer to access content on the internet).
Example:
Proloquo2Go is an application that allows students with cognitive and/ or speech difficulties to express themselves. The student selects images/symbols representing what he/she wants to express and the application oralises it.
The Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in schools have been subsumed in the Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA). Now ICT in Schools is a component of the RMSA. The Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in Schools was launched in December, 2004 and revised in 2010 to provide opportunities to secondary stage students to mainly build their capacity on ICT skills and make them learn through computer aided learning process. The Scheme is a major catalyst to bridge the digital divide amongst students of various socio economic and other geographical barriers. The Scheme provides support to States/UTs to establish computer labs on sustainable basis.
The National Programme on School Standards and Evaluation (NPSSE), known as Shaala Sidhdhi is a comprehensive instrument for school evaluation leading to school improvement. Developed by the National University of Educational Planning and Administration (NUEPA), it aims to enable schools to evaluate their performance in a more focused and strategic manner and facilitate them to make professional judgments for improvement. The programme‟s objective is to establish and refer to an agreed set of standards and to provide clear pathways for each school for self evaluation, by focussing on key performance domains and their core standards for school evaluation. The structure of the Framework is simple yet flexible and lends itself to both self and external evaluation. A web portal for the framework has been launched by Hon‟ble HRM on 7.11.2015 which will enable all schools to engage in self-evaluation in the 7 key domains under the Framework. The results of the evaluations will be available on a public platform along with the school report card.
E-Pathshala has been developed by NCERT for showcasing and disseminating all educational e-resources including textbooks, audio, video, periodicals and a variety of other print and non-print materials through website and mobile app. The platform addresses the dual challenge of reaching out to a diverse clientele and bridging the digital divide (geographical, socio-cultural and linguistic), offering comparable quality of e-contents and ensuring its free access at every time and every place. All the concerned stakeholders such as students, teachers, educators and parents can access e-books through multiple technology platforms i.e. mobile phones (android, ios and windows platforms), and tablets (as e-pub) and on web through laptops and desktops (as flipbooks). All the NCERT books have been digitised and uploaded. Currently the e-contents are available in Hindi, English and Urdu. States/ UTs are being approached to digitise and share all textbooks in Indian languages through this platform, which will be done in a phased manner. The Web portal and Mobile App of e-Pathshala was launched by Hon‟ble HRM during the National Conference on ICT in School Education on 7th November, 2015.
4.5 Future technologies: Universal Design: Meaning & Scope
Universal design is the process of creating products that are accessible to people with a wide range of abilities, disabilities, and other characteristics. Universally designed products accommodate individual preferences and abilities; communicate necessary information effectively (regardless of ambient conditions or the user's sensory abilities); and can be approached, reached, manipulated, and used regardless of the individual's body size, posture, or mobility. Application of universal design principles minimizes the need for assistive technology, results in products compatible with assistive technology, and makes products more usable by everyone, not just people with disabilities.
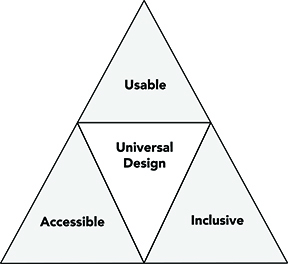
According to the Center for Universal Design, UD is "the design of products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design." To narrow the scope, this definition can be modified. For example, to apply UD to teaching and learning activities, this basic definition can be modified to "the design of teaching and learning products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design."
Characteristics of any UD product or environment are that it is accessible, usable, and inclusive
Typically, products are designed to be most suitable for the average user. In contrast, products that are designed according to principles of universal design are designed to be usable by everyone, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design (Connell et al., The Principles of Universal Design).
UDL Principles
A Universally Designed for Learning (UDL) curriculum in formal and informal settings “reflects an awareness of the unique nature of each learner and the need to address differences” by offering
· Multiple means of engagement. For purposeful, motivated learners, stimulate interest and motivation for learning. UDL guidelines under this principle promote the development of curriculum and instruction that includes options for perception; language, expressions, and symbolism; and comprehension.
· Multiple means of representation. For resourceful, knowledgeable learners, present information and content in different ways. UDL guidelines under this principle promote the development of curriculum and instruction that includes options for physical action, expressive skills and fluency, and executive functions.
· Multiple means of action and expression. For strategic, goal-directed learners, differentiate the ways that students can express what they know. UDL guidelines under this principle promote the development of curriculum and instruction that includes options for recruiting interest, sustaining effort and persistence, and self-regulation.
Universal design typically results in product features that benefit a variety of users, not just people with disabilities. For example, sidewalk curb cuts, designed to make sidewalks and streets accessible to those using wheelchairs, are today often used by kids on skateboards, parents with baby strollers, and delivery staff with rolling carts. Similarly, a door that automatically opens when someone approaches it is more accessible to everyone, including small children, workers whose arms are full, and people using walkers or wheelchairs.
At the Center for Universal Design at North Carolina State University, a group of architects, product designers, engineers, and environmental design researchers established the following set of principles of universal design to provide guidance in the design of environments, communications, and products (Connell et al., 1997). They can be applied to academic environments, communications, and products.
1. Equitable Use. The design is useful and marketable to people with diverse abilities. For example, a website that is designed so that it is accessible to everyone, including people who are blind, employs this principle.
2. Flexibility in Use. The design accommodates a wide range of individual preferences and abilities. An example is a museum that allows a visitor to choose to read or listen to the description of the contents of a display case.
3. Simple and Intuitive Use. Use of the design is easy to understand, regardless of the user's experience, knowledge, language skills, or current concentration level. Science lab equipment with control buttons that are clear and intuitive is a good example of an application of this principle.
4. Perceptible Information. The design communicates necessary information effectively to the user, regardless of ambient conditions or the user's sensory abilities. An example of this principle being employed is when television programming projected in noisy public areas like academic conference exhibits includes captions.
5. Tolerance for Error. The design minimizes hazards and the adverse consequences of accidental or unintended actions. An example of a product applying this principle is an educational software program that provides guidance when the user makes an inappropriate selection.
6. Low Physical Effort. The design can be used efficiently and comfortably and with a minimum of fatigue. Doors that are easy to open by people with a wide variety of physical characteristics demonstrate the application of this principle.
7. Size and Space for Approach and Use. Appropriate size and space is provided for approach, reach, manipulation, and use regardless of the user's body size, posture, or mobility. A flexible science lab work area designed for use by students with a wide variety of physical characteristics and abilities is an example of employing this principle.
Universal Design Scope:
· Universal Design helps teachers plan learning to meet the diverse and variable needs of all students. Flexible supports for learning can be embedded into an environment and made available to everyone. Hidden barriers to learning can be identified and minimised. Universal design can be used beyond the classroom to underpin the design of more inclusive homeschool communications, professional learning options, and community events.
· Universal Design for learning helps teachers optimize their teaching and learning. Use it to create a more inclusive, flexible environment, where barriers to learning are minimized with supports and options available to all students.
· Overview of the value of using captioned or subtitled videos to support literacy across the curriculum. Provides all students with alternative access to content in videos.
Lot of modern technology is ideally suited for deaf culture. Text and instant messaging, for example, are beneficial to deaf people because they allow conversation between people regardless of whether or not they are deaf and they do not require the use of sign language. However, with in the deaf community not everyone is accepting or open to technology bridging the gap between the hearing and the non-hearing. There are two groups within the community with differing opinions on the matter. There are people who refers to themselves as deaf with the lower case “d” and there are the deaf with a capital “d”. The deaf group is one that takes pride in traditional forms of communication amongst deaf people and limits the use of technology as a way of communicating. For the deaf, technology enhances deaf culture and is positively looked upon.
Deafness can have a major impact when it comes to learning, which makes deaf education an area that greatly benefits from the use of technology. When in a classroom environment, speech-to-text systems can prove beneficial to students without hearing. These systems convert spoken words into real-time, displayed text that students can read on their computers or on a screen that is displayed to the class. In addition to the real-time display of text, these systems also provide a print out or text file of the lecture.